11 Published Papers Highlight Crucial Radionuclide Dispersion
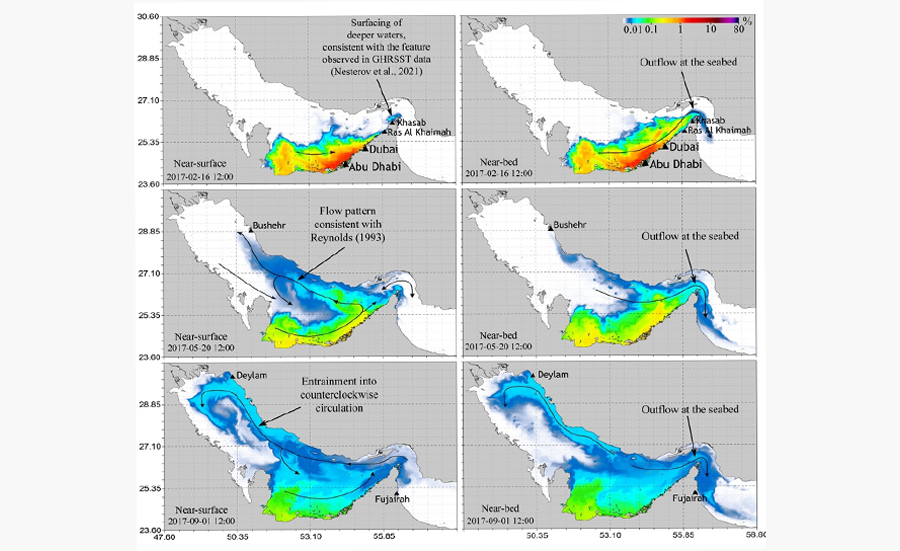
In a significant stride towards achieving the UAE’s peaceful nuclear goals, Khalifa University’s Emirates Nuclear Technology Center (ENTC), in collaboration with the Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation (FANR) and the French Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire (IRSN) has successfully completed Phase 1 of the Numerical Modelling of Radionuclides Dispersion (MORAD) research program. The collaboration has yielded 11 published papers, highlighting crucial environmental aspects.
Playing a vital role in supporting the UAE’s peaceful nuclear energy sector, the primary objective of the MORAD program is to augment the UAE’s capacity to simulate the dispersion of radionuclides across marine, atmospheric, and continental environments as well as regional and local features. In addition to FANR’s contribution to the ENTC fund, the Federal Authority also funds two projects, which include the MORAD project, and the OECD-ATLAS-III project, currently in its second phase, after successfully completing Phase I in 2021. Both projects foster a proficient workforce among UAE Nationals alongside Khalifa University’s Nuclear Engineering Master’s program which also remains one of the key factors shaping the UAE’s nuclear capabilities for a science-oriented workforce.
Dr. Yacine Addad, Deputy Director, Emirates Nuclear Technology Center, and Associate Professor, Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering, Khalifa University, said: “In light of the UAE’s commencement of its peaceful nuclear program, marked by the construction of four nuclear power plants, Khalifa University remains committed to bolstering the country’s human capital in the field of nuclear safety. The completion of Phase-1 of the OECD-ATLAS-III Project in 2021 and Phase-1 of the MORAD research program in 2024 aligns with the country’s overarching aspiration for optimal and managed energy mix, in addition to diversifying the Emirate’s economy. The ENTC’s success has set the path toward mitigating the impact of this newly embraced sustainable energy source on the natural environment, while new research continues to enhance the collective understanding of radionuclide dispersion and its environmental impact, locally and globally.”
Collaboration with FANR continues, following Khalifa University’s successful participation in Phase 2 of the OECD-ATLAS project. During this phase, researchers achieved important safety analysis milestones by validating and verifying safety analysis codes and assessing the thermal-hydraulic behaviors of Advanced Power Reactor 1400 MWe (APR1400). The ENTC research team is now focused on implementing Phase 3 activities within the ATLAS project to produce numerical results for pre-test and post-test simulations.
Moreover, this project aims to broaden its scope by comparing two main system codes, the RELAP5 and TRACE computer programs that simulate and analyze the behavior of nuclear power plants under different operating conditions. In order to help improve the safety and efficiency of nuclear power plants, the project also aims to develop and utilize specialized facilities at Khalifa University, for conducting specific tests and experiments.
Alisha Roy
Science Writer
16 April 2024